TPC-DS Benchmark using Trino with Ceph Object Storage S3 Select
Introduction ¶
In this article we analyze the results of performance benchmarks conducted on Trino with the Ceph Object S3 Select feature enabled, using TPC-DS benchmark queries at 1TB and 3TB scale. We demonstrate that, on average, queries run 2.5X faster. In some cases, we achieved nine times improvement with a network data processing reduction of 144TB compared to using Trino without the S3 Select feature enabled. Combining IBM Storage Ceph's S3 Select with Trino/Presto can enhance data lake performance, reduce costs, and simplify data access for organizations.
We would like to thank Gal Salomon and Tim Wilkinson for conducting the TPC-DS benchmarking and providing us with these results.

What is Trino? ¶
Trino is a distributed SQL query engine that allows users to query data from multiple sources using a single SQL statement. It provides data warehouse-like capabilities directly on a data lake.
What are the difference among Trino, Presto and PrestoDB? ¶
You may have encountered references to Trino, Presto, and PrestoDB, all of which originated from the same project. Presto was the initial project from Facebook, which was open-sourced in 2013. PrestoSQL became a community-based open-source project in 2018 and was rebranded to Trino in 2020.
Presto is an essential tool for data engineers who require a fast query engine for their higher-level Business Intelligence (BI) tools.
Why Choose Ceph for S3 Object Storage? ¶
- Ceph provides a first-class, highly compatible S3 API for on-premises deployments.
- Ceph confidently meets the needs of critical large-scale installations and the ever-growing demand for data. Its performance scales alongside capacity, resulting in substantial cost savings and the ability to manage exponential data growth.
What enhancements does Ceph bring to data query tools like Trino, Presto? ¶
Ceph provides the S3 API S3 Select feature. S3 Select significantly improves the efficiency of SQL queries of data stored in S3-compatible object storage. By pushing the query to the Ceph cluster, S3 Select can dramatically enhance performance, processing queries faster and minimizing network and CPU resource costs. S3 Select and Trino are horizontally scalable, handling increasing data volumes and user queries without sacrificing performance. Trino's support for SQL and S3 Select's ability to query data in place enables users to access and analyze data without complex data movement or transformation tasks.
Ceph's Object Datacenter-Data-Delivery Network (D3N) feature uses high-speed storage such as NVMe SSDs or DRAM to cache datasets on the access side. D3N improves the performance of big-data jobs running in analysis clusters by accelerating recurring reads from the data lake or lakehouse.
TPC-DS benchmarks using Ceph + Trino ¶
Test Procedure ¶
We executed the following 72 TPC-DS queries at three different scale factors, 1TB, 2TB and 3TB, to characterize performance and resource consumption. The datasets were in uncompressed CSV format. We executed each query numerous times with and without S3 Select and ensured consistent results by monitoring the standard deviations for each run.
If you’re interested in exploring this topic further, please check out Gal Salomon's GitHub repository, where you will find instructions on how to set up a testing environment with Trino and Ceph. Instructions are also provided for the TPC-DS benchmarking tools used for this benchmark.
Test Environment ¶
The hardware used for the benchmark was the following:
- Trino client (driver) nodes
- Trino Version: 405
- 3x Dell R630
- 2x E5-2683 v3 (28 total cores, 56 threads)
- 128 GB RAM
- Ceph cluster nodes
- OS: RHEL9.2
- Ceph version: 18.2.0-110.el9cp (Reef)
- 3x Dell R630 Monitor / Manager nodes
- 2x E5-2683 v3 (28 total cores, 56 threads)
- 128 GB RAM
- 8x Supermicro 6048R OSD / RGW nodes
- 2x Intel E5-2660 v4 (28 total cores, 56 threads)
- 256 GB RAM
- 192x BlueStore OSDs
- 24 2TB HDD per node
- 2x 800G NVMe SSDs for WAL/DB per OSD node
Tunables ¶
These S3 Select settings were adjusted:
- hive.max-split-size The maximum size of a single file section assigned to a worker. More minor splits result in more parallelism and thus can decrease latency but incur more overhead and increase load on the system. Testing began with 4MB, 8MB, 16MB, 32MB, 64MB, and 128MB values but we eventually settled on 128MB for all tests.
- hive.max-splits-per-second The maximum number of splits per second generated per table scan. It can be used to reduce the load on the storage system. There is no default limit, so Trino maximizes the parallelization of data access. All testing was performed using 10K for this setting.
Concurrency ¶
The Trino engine processes complex queries by dividing the original query into multiple parallel S3 Select requests. These requests split the requested table (an S3 object) into equal ranges that are then distributed across our Ceph cluster's RGW service. The load balancer efficiently channels requests among Ceph Object Gateways, ensuring optimal performance and scalability for our data processing needs.

Test Results ¶
This next section provides an overview of TPC-DS benchmark results. These results help us understand how the Ceph Object S3 Select feature yields substantial benefits when working with CSV datasets. The benefits include improved query times and reduced data processing. We have included a diagram below that shows the total network traffic reduction achieved by using S3 Select. We can save 144TB of network traffic by utilizing this feature.

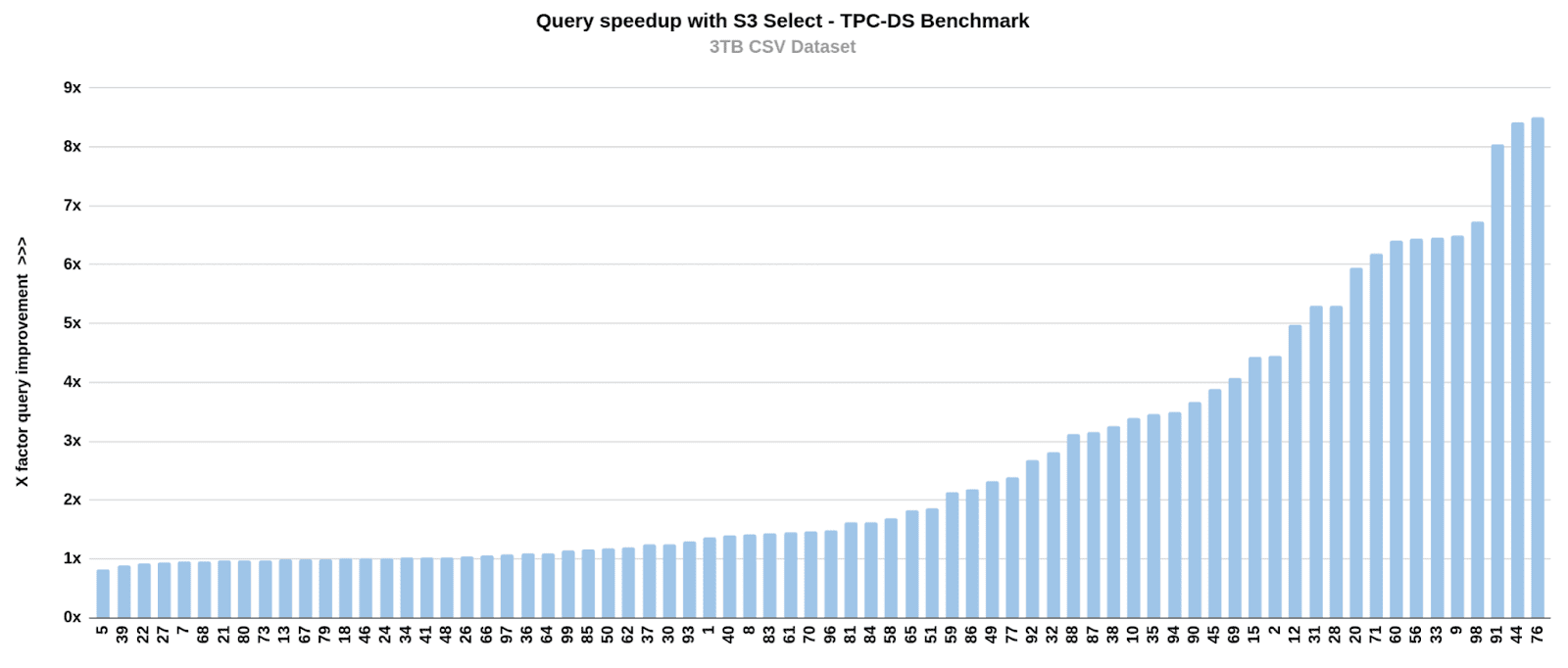
The following graph shows the per-query speedup achieved using S3 Select for the 3TB scale dataset. The X axis value is the query number from the above repository and the Y axix value is the speed improvement for each query. During testing we observed that enabling S3 Select improved all 72 queries. The query acheiving the most speedup was 9 times faster, and the overall average improvement was around 2.5x.

When S3 Select is enabled we offload computational work to the Ceph Object Gateways, so as expected they saw increased CPU usage when executing the queries with S3 Select enabled. However, the CPU utilization remained at an acceptable level Memory demand increase with S3 Select enabled was barely noticeable, with an average increase 2.50%. Pushdown can process objects of any size since it does so in chunks without preloading the entire object.

Query number 9 was able to reduce the network data processing by 18TB. The total reduction in processed data across all 72 queries was 144 TB when enabling S3 Select.

Summary and What’s Up Next ¶
In this post, we shared the results of our benchmark testing, where we ran 72 TPC-DS 72 queries at 1TB and 3TB scale. We have found that utilizing Ceph Object S3 Select pushdown performance optimizations enables queries to complete more quickly than before with significantly lower resource demands. With Trino and S3 Select, you can push the computational work of projection and prediction operations to Ceph, achieving up to 9x performance improvement in query runtime, with an average of 2.5x. This significantly reduces data transfer across the network, saving 144TB of network traffic for the 72 executed queries. Organizations can enhance data lake performance, educe costs, and simplify data access by combining Ceph S3 Select with Trino and Presto.
The authors would like to thank IBM for supporting the community with our time to create these posts.